If you are keen on music, you might be aware that an equalizer is important in any audio content. An EQ plays a great role in equalizing your music. It is flexible and serves as a filter through which you can make different alterations to your audio content. Additionally, an EQ allows you to adjust the volume levels of different frequencies.
For instance, you can increase or lower the bass or treble of your car’s music system using an EQ. Generally, a Parametric EQ makes diverse changes in the frequency spectrum whether subtle or extreme.
These changes are made according to the specific sound of the instruments featured in a mix. If parametric EQ is a new term to you, this article is timely. Keep on reading as we are going to describe it in detail and everything about it that you need to know.
What Is Parametric EQ?
A parametric EQ is a mainstay that boosts a frequency spectrum or makes it distinct. It comes in handy in a live sound or recording because it keeps every parameter controlled. This controls the frequency of the audio signal. There are three parameters EQ’s through which you can get the different equalizations, and here is a discussion of each.
Fully Parametric
This is a parametric that gives control over the boost or cut amount being applied for every frequency band. These bands could be the cut-off frequency for the high and low bands or the frequency center of the midrange bands.
This type of parametric EQ controls the bandwidth whose responsibility is to identify any range of affected frequencies. Additionally, a fully parameter EQ determines the Q which happens to be the ratio between the bandwidth and the center frequency. Even though the bandwidth control and the Q control are not similar, the two have a similar accomplishment.
Semi Parametric
This is a parametric equalizer whereby both the frequency and gain can be adjusted while the bandwidth and Q remain fixed. A semi-parametric features at a preset value.
Quasi Parametric
These are the variations that take place on the semi-parametric. The role of a quasi-parametric EQ is to gain three Q settings adjustments and offer frequency for the same. However, this equalizer can’t do this to a bandwidth. A good example of quasi parametric is the midrange EQs found on the mixing consoles.

Understanding Q
This is the ratio of bandwidth to the center frequency in the equalizer is what is referred to as the Q. It is offered by the parametric EQ and it helps you to boost or cut different frequency ranges whether wide or narrow. Going back to the ratio, if the center frequency happens to be fixed, the bandwidth becomes inversely proportional to the Q. In other words, the bandwidth narrows as the Q raises.
One major benefit of a narrow bandwidth is to filter out any tones that could be unpleasant. For example, you can isolate an annoying ringtone interfering with your audio with a bandwidth. Another name of this bandwidth filtering is a notch filter. This means that you can easily remove any altered frequency and leave the instruments in the mix intact.
Narrow bandwidths are also great in improving the best aspects of an instrument’s sound. You can do the instrument sound enhancement without leaving the rest of the mix overpowered.
On the other hand, a broad bandwidth handles larger frequencies. Both the broad and narrow bandwidths work together to give you the effect you expect. It is important to understand that broad bandwidth has a big data-carrying capacity.
There is a difference between bandwidth and Q because as one goes up the other comes down. This is to say the Q increases as the bandwidth decreases.

Shelving EQ
This is the boosting or cutting off of a band of frequencies either in the high frequency or low-frequency end of the spectrum. In shelving equalizers, the low-end frequency is responsible for filtering out all frequencies that are below a particular frequency cut off. On the other hand, the high-end frequency functions directly opposite.
It passes all the frequencies that are above a particular cutoff frequency. In most cases, the frequencies that extend above the cutoff are cutoff following as per the predetermined curve.
Multiband parametric EQs give bands that are low and high and they can be switched shelving filters. Studio channels is a good example, the high and low bands are the filters and the mid-band is fully parametric.
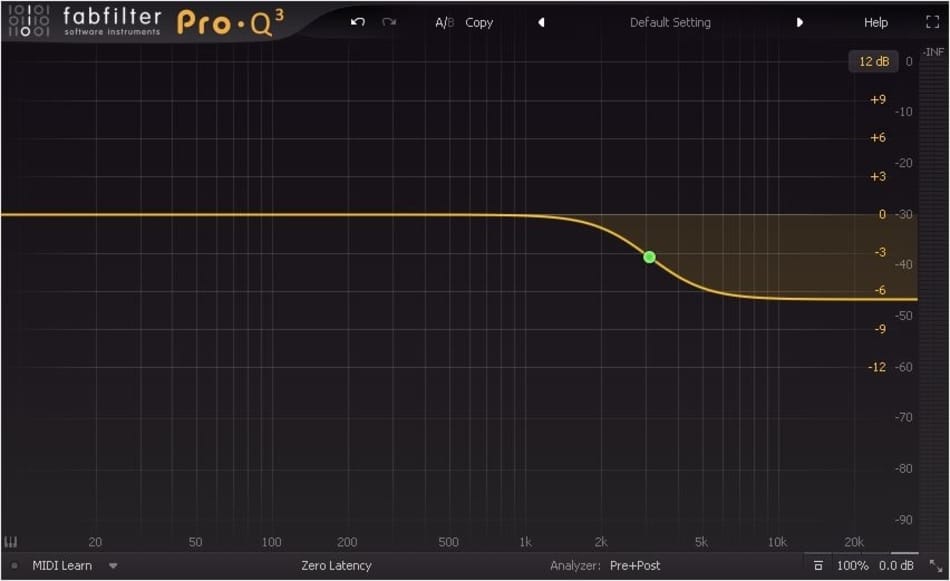
How to Use Parametric EQ
Sometimes you can have a muddy mix because of a frequency cluster. However, you will have more control over the equalization process thanks to the bandwidth option. The option helps you focus on a particular frequency or frequencies.
This group could have a high Q or a low Q. Therefore, a parametric EQ can easily get rid of the unwanted frequencies and enhance other signals with a gentle touch. However, this depends on other resonations of the specific instrument that is being used in the mix. Here are some simple explanations of how you can use a parametric equalizer.
1. Use the high-end and low-end filter
There is always a high-end and low-end function on many software programs. The high filters out any frequency exceeding 100 Khz. On the other hand, the low-end frequency filters out any frequency that is above 10Khz. You can use these buttons to get rid of any harmonics that could interfere with your audio whether high or low.
2. Determine the Frequency
In software programs, you can cut or boost 3 to 7 frequencies at the same time. The frequencies are also known as the bands and you can start one at a time. You do this by gently touching the frequency spectrum screen to turn on the bandwidth.
3. Establish the Bandwidth
It is in the bandwidth that the frequency is boosted or cut. As mentioned earlier the bandwidth is also known as the Q. You can set the Q to as low as 1/30 of one octave. If you have more octaves the band can give you a detailed basic tone shaping. If you want to get rid of frequencies that may be problematic, you just narrow down the Q. The widening or narrowing of the Q is done by respectively lowering or raising the number.
4. Cut or Boost the Band
If you are done with setting the Q and the frequency, it’s time to boost or cut the bandwidth. You do this by using the gain function to cut the band by lowering the gain to below zero and raising it above zero. Be keen to gently make adjustments that are minimal until you get the sound you desire.
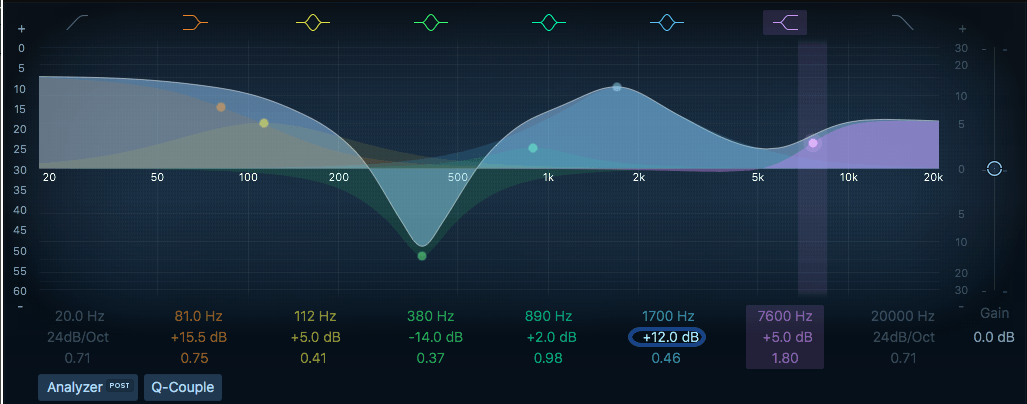
What Are the Benefits of Parametric EQ?
In case you are wondering why parametric EQ is important, here are some of its benefits:
1. Feedback cancellation – If you have ever been to live music events, you might have heard some shrieking sounds in the background. This is mostly when the mics are close to the speakers. Parametric equalizers come in handy in solving such problems by filtering the frequencies behind them.
2. Studio monitors tuning – There are peaks and dips in any speaker at different frequencies. If you have a home studio, you require a speaker that has a flat response. It is at this point that parametric equalizers will flatten the peaks and dips.
3. Elimination of unwanted noise – Parametric equalizers is mostly used by sound producers to cancel any background noise. This could be the piano pedal or the noise produced by guitars when they are picking.
4. Enhancement of studio performance especially in recording, mixing and production
5. Helps in frequency adjustment
6. It is deliberate and complex in its functionality
Examples of The Best Parametric Equalizers
SSL 4000 Series
This parametric equalizer is flexible and there you can use it on any instrument and acquire the results you expect. The 4000 series is available in two iterations namely: G-channel equalizer and the E-channel equalizer. Each of these equalizers has its properties. For instance, a G-channel EQ narrows the bandwidth slope as you cut or boost.
Another name for this equalizer is the proportional Q style. The E-channel on the other hand is not altered by the cutting or boosting thus it remains constant. This equalizer is also known as the constant Q and it is a famous unit and it’s great in a recording.
iZotope Neutron 3
This equalizer is a giant because it allows you to insert up to twelve EQ band nodes by simply clicking on the EQ curve. Each band has a separate operation menu featuring dynamic and static mode controls. Also, you will get all you want with this parametric equalizer because it easily identifies any problem-causing frequencies.
Several features make Neutron 3 to be among the best equalizers. It has a soft saturation mode that adds warmth to your music. Also, with this equalizer, you can easily locate different frequencies that you are interested in.
Waves Q10
You will get different equalization options with the Wave Q10 thanks to its ten bands. There are six different types of filters in each band and it gives you complete control of the frequency, gain, and Q. The best part about this unit is that each of its bands features a flexible shaping signal. Also, the Q10 equalizer features large cuts and boosts thus giving you the best results.
Eiosis AirEQ
Easy to use, character and strength parameters are some of the things that define this parametric equalizer. It also has a unique design that will make a statement in your studio. You should expect quality, clear and straightforward sound if you choose this equalizer. Also, it processes fast and that’s why it is best for post-production, mastering, and mixing.
Sound theory Gullfoss
The intelligence that Gullfoss boasts is unmatchable. This is because before preparing any audio, the equalizer listens to the signal first and makes the right decisions. This unit is also swift in fixing unsolvable issues that would have taken you much time and skills to resolve. This parametric equalizer also fixes any balancing problems between different elements of sound even without accessing the particular track.
Fabfilter Pro-Q 3
Give this parametric equalizer any job and it will deliver thanks to its flexibility. It is best in mixing and mastering and boasts an excellent sound quality. It has 24 bands all of which work towards handling even the most complex tasks with utmost convenience.
You have the independence of setting each band the way you want by using any curve type independently. The other features of this parametric equalizer include spectrum analysis, detection of a collision, dynamic equalization.
Buyers Guide to A Good Parametric Equalizer
Choosing an equalizer that will serve you for long is not a walk in the park. The market is full of different models and therefore you need some knowledge on how you can pick the best. Here is a buyer’s guide that will help you select:
Budget
This is the first thing to consider because you can only get what you have money for. Audio pieces of equipment are priced differently depending on features. You should therefore do a good market research and know what you can afford. However, you can never lack a model that will go with your budget.
Additionally, some retailers offer payment options and if you are lucky you can pay in installments. However, you should consider the reason why you are buying an equalizer. For instance, if it’s for commercial purposes, there will be no harm in spending more.
Parametric EQ’s Hardware Vs Plugin
You have two options when buying an equalizer. You can go for hardware EQ or plugin EQ. The EQ plugin has original designs that make them effective in digital programming and processing. They are also more practical compared to the equalizer hardware. Also, you can insert this EQ plugin on many audio tracks without limitation.
The case is different for the EQ hardware. The best thing about these plugins is that their upkeep is not complicated because you won’t have to carry out any physical maintenance. The EQ plugins are also cheaper compared to the EQ hardware.
Styles of Equalizers
The market is full of different equalizers and that’s why you should be sure about the style you want. Their difference is in functionality, audio quality, and applications. You should therefore establish which style will suit your need for an equalizer before proceeding with the purchase. You don’t want to buy something that you will regret.
For example, if you want a commercial parametric equalizer, you should look for one with diverse features.
Equalizer’s Inputs and outputs
This is another critical factor that you should consider heavily. You can have a stereo or a mono equalizer. The mono one has only one input channel and one output channel. On the other hand, a stereo equalizer has two channels.
Number of Bands
The number of bands is another important factor when it comes to buying a parametric equalizer. Each band that an equalizer has serves as a filter and therefore it can significantly affect the quality of the audio content. An equalizer with a big number of bands has a complex yet straightforward graph compared to the one with fewer bands. Also, they are usually highly-priced because of their highly reliable performance.
Applications
There are three main applications for equalizers. They include recording studios, car audio, and public address or live sound. It is therefore important to pick a parametric equalizer that will match what you do. For example, if you want an EQ for a live event, you buy an equalizer that removes any resonation frequencies in an acoustic space with ease. On the other hand, an equalizer for car audio should have reliable bass, treble, and mid controls. It should also have higher frequencies.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s the meaning of the Q parameter in EQ?
It is the quality factor meaning it is the ratio of the bandwidth of the EQs filter to a resonant frequency. If the Q factor is high, the boost or cut will be low
2. What is a high pass filter in EQ?
This is a filter that passes through the high frequencies found above the cutoff frequency. Its responsibility is to ensure that any content with a low frequency is removed from the audio signal that is below a particular cut-off point.
3. How many types of filters are there in a parametric equalizer?
A parametric equalizer has 6 filters and here is a list of them.
- Bell filters
- Shelving filters
- Notch filters
- Band-pass filters
- High-pass filters
- Low-pass filters
4. What is a graphic equalizer?
A graphic EQ typically consists of a predetermined bands centered around set frequencies with set Q factors (which can be boosted or attenuated). They generally give users a graphic visual representation.
5. What is the difference between graphic and parametric EQ?
A graphic EQ offers gain control over a fixed set of frequency bands whereas a parametric EQ allows enhanced gain control (over any frequency within a range). The parametric EQ also enables users to control the bandwidth or Q of each filter.
Conclusion
We have discussed everything you need to know about a parametric equalizer. You now know what it is and its benefits. Additionally, we have mentioned some of the best equalizers available in the market and most importantly the factors you should consider before purchasing one. We hope the article has been informative and will help you in whichever audio field you are in.
You may also be interested in:
