Despite the fact that digital signal processing (DSP) has indeed been available for several years in the IT sector, it is still being used in our everyday audio devices. To improve the client experience, DSP is heavily employed in smart devices such as the Amazon Echo, Apple Air Pods, and Google Home.
What exactly is DSP Audio? Is it really necessary and beneficial to the audio experience? In this article, we’ll look at DSP and how much it influences our audio experience.

What Is DSP?
The term DSP refers to a digital signal processor. Headphones, smart speakers, cellphones, automobile entertainment devices, studio audio gear, and much more all contain the technology. It’s certainly one of the most important features of modern audio equipment.
You’re likely aware with the concept of a processor from a computer’s CPU, which is built to perform multiple tasks. A digital signal processor (DSP) is a system that is specialized for number-crunching digital signals such as audio. They’re made to do mathematical operations like addition and subtraction quickly and efficiently while consuming little energy.
DSP chips are available in a wide range of sizes, costs, and performance levels. From multi-channel processors in professional studio equipment and cars to tiny low-power circuits for smart speaker voice commands, the technology has progressed. They’re utilized to accelerate the implementation of audio-related computations while using less energy than a traditional CPU.

Your smartphone, for instance, has a DSP that can decode MP3 files, perform active noise suppression calculations, increase the volume of your music, and detect your voice. Wireless headphones have DSP units that turn Bluetooth transmitted data back into audio frequencies, while in-home cinema speakers have DSP units that decoding data streams into a surround sound impression. There’s almost probably a DSP in it if it’s processing audio.
How DSP Affect Sound Quality
DSP can aid with sound quality in a variety of methods. Here are the most important aspects of audio quality that DSP enhances:
Improve Frequency and Dynamic Spectrum
In general circumstances, digital transmissions have a higher frequency or dynamic range than analog ones.
The dynamic spectrum of a common commercial analog cassette tape, for example, is 50 to 70 dB. When an analog signal is passed through a 16-bit analog-to-digital processor, its dynamic range is extended to 90 to 95 dB.
DSP also has the capacity to increase the frequency range. In other words, higher highs and lower lows are audible.
Help In Conversion
When a musician plays a sound, they send analog impulses to the microphone, which the microphone collects. The signal from the microphone will be sent to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). It will deliver the analog signal to DSP once it has been converted to digital.
The output format (e.g., MP3, FLAC, WAV, etc.) will be encoded and saved to memory by the DSP. Other operations, like as echo cancellation, noise control, and others, can be done with a sophisticated DSP system.

The DSP will take the information from the memory, decode it, and transport it to the digital-to-analog conversion when you playback the recording (DAC). After that, the DAC will transform the signal to analog and send it to the speakers.
Remove Unnecessary Echo
Among the most important achievements that DSPs should take credit for is echo elimination. Your laptop or phone can recognize a ‘copy’ of the transmission is just transmitted as noises that it receives after a short period of time utilizing digital signals. The DSP will erase that duplicate from the next data supplied to the DAC.
While analog equipment may perform the same function, DSP can do much faster and with less power, making it perfect for compact devices such as wireless headphones and IEMs.
Noise Control
Through the signal processing step, the electronic elements in listening gadgets adjust the voltages, resulting in sound reproduction. The undesired noise you hear, such as hissing or humming is, nonetheless, an unavoidable element of the signal processing output.
The DSP can specify a minimum sound frequency that should be sent to the speakers and DAC. Noises such as humming and hissing have a lower frequency, which allows digital signal processors to filtering them out.
Gain Control
Gain control is comparable to how you manage the volume on your phone while on the phone. If the volume on your phone is too low, you won’t be capable of distinguishing the person on the receiving end. However, if you turn up the volume too high, they’ll sound distorted.
In between highest and lowest levels, there’s a sweet spot in which you can clearly hear the person’s voice, whether they’re speaking properly or yelling.
The “sweet spot” is discovered by matching the input signal strength to the level that the outputs (headphones or speakers) can readily handle without reducing volume or distortion. The DSP can take this always pleasant spot and balance the dynamics to drastically improve the listening quality.
Automatic Sound Adjustment
Digital signal analysis’ rapid growth has a tremendous impact on not only sound quality, but also the complete listening experience. In the last decade or two, the DSP became the cornerstone of modern sound devices.
The AirPods Pro’s Adaptive EQ feature and Nuraphone’s Personalized Sound feature, for example, use the size of your ear cavities to determine the best equalization settings, resulting in a more immersive and authentic listening experience.
How DSP Audio Works
DSPs can’t function on their own. DSP requires both a DAC and an ADC to transform an input from digital to analog and vice versa.
When you speak into a microphone, your voice is captured as an analog signal, which will then be evaluated from an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). The ADC translates the voices and sounds picked up by microphone into binary 0s and 1s that computers, such as the DSP, can understand.
Once the ADC has appropriately altered the signal, it will be transmitted to the DSP. Once it reaches the DSP, the signal will go through a custom equalization, noise reduction, encoding, bass enhancement, echo cancellation, and other operations.
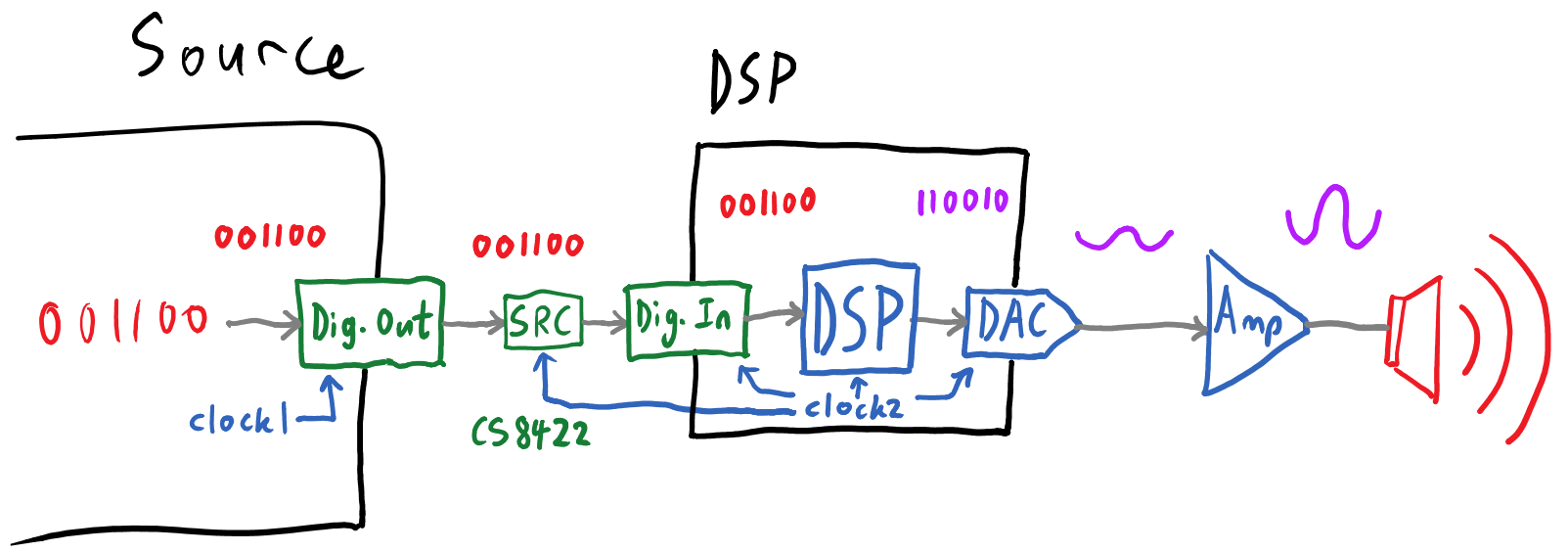
To perform the activities listed above, a DSP must include several critical elements:
- Data Memory: The input that requires to be handled is saved here.
- Program Memory: It holds the data-processing software that the DSP will employ.
- Input/Output: The DSP’s means of collecting and transmitting data from and to the outside world.
- Computer Engine: Analyze the signal using details from the program and data memory.
The most basic methods of DSP include echo cancellation and noise cancellation. Noises received by microphones are processed by the DSP of ANC headphones, which creates counter-frequencies to cancel them out.
Digital signal processors can remove echoes by ‘listening’ for a copy of the wave they just generated. They erase the duplicated signal and provide the ‘clean’ digital output signals to the DAC when they discover it. The DAC turns it to an analog signal that can be used in the real world after that.
How DSP Will Impact Your Music Listening Forever
DSPs are important because they are an integral part of current audio equipment, ranging from car speakers to headphones and professional gear. A good DSP will give you the processing power to run high-quality effects like on-device EQs, active noise cancellation speech recognition, and surround sound. Premium DSPs also use extremely little power, extending the battery life of your devices and allowing you to listen for extended periods of time.
DSP capabilities, on the other hand, aren’t listed on many, if any, spec sheets. DSPs are often included with the Bluetooth chip’s capabilities in headphones, although other devices often include DAC, ADC, and speaker driving capabilities, as well as the DSP, on a single chip. Instead of seeking for processing specifications, look for DSP capabilities in other product features.
The Apple AirPods Max, for example, features a DSP to continuously alter the headset’s functionality in order to enhance audio quality. Sony’s 360 Reality Audio can also modify its output using a map of your ear to produce its enchantment.

Even diehard audiophile geeks use custom DSP boxes to adjust simulated surround sound systems included in products, as well as correct efficiency for headphones and bookshelf speakers. You can analyze the output of your audio gear in any setting using a DSP unit and a suitable microphone, and instantly adjust the output to sound the way you want it to sound.
Basically, using a modern DSP eliminates the necessity to hope that your audio equipment will sound good; instead, you may compel it to sound nice at any time by having the electronics correct for flaws on the fly. This is a significant change from the past, when the usage of DSP boxes was limited to hobbyists and obsessives. Not any longer.
Why Do Some Listeners Dislike DSP Audio?
Digital signal processor improves the quality of sound listening in a variety of ways. However, some audiophiles have been put off by a variety of drawbacks when it comes to using DSP in their equipment.
Difficulties With Sound Accuracy
Clarity is important to many audiophiles. The technique of analog-to-digital conversion, nonetheless, results in a loss of sound accuracy. Many audiophiles claim to be able to tell the difference between a sophisticated, colored sound wave and a binary code of 0s and 1s.
Despite the fact that digital converter is a binary representation of an analog signal, most musicians and producers aren’t nostalgic for the days before digital. Most musicians, engineers, and producers, are well aware that the vast majority of listeners would be unable to tell the difference between digital and analog sound.
The primary goal of digital signal processor is to fix any sound defects. If the source recording is missing bass, for example, DSP can provide it using technological wizardry. The same rationale holds true for a song’s vocals, mids, and highs: DSP can only improve them.
DAC vs DSP
There are a few common misconceptions about digital signal processing (DSP) and digital analog converter (DAC). Some people can’t detect the difference between the two, while others are undecided about whether to buy a traditional DAC or one with designed DSP.

If you’re one of the individuals who is still bewildered, don’t worry. For your consideration, we’ve created a list of frequently asked questions:
1) What Is The Difference Between DAC & DSP?
As the name implies, a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) is a device that converts a digital input into analog output. If it processes the signal in any way, it isn’t a perfect DAC.
Many individuals may be perplexed by the fact that DSPs are frequently seen in systems with both ADC and DAC.
The reason for this is because digital signal processors (DSPs) only function with digital or binary data, but the rest of the world is analog. To put it another way, DSPs require an ADC for data analysis and a DAC for info use in the actual world.
2) Should You Choose DACs With Integrated DSP?
The short answer is that DACs with custom DSP are the best option. It’s possible that having DSP incorporated into your DAC will improve the clarity of your audio, regardless of what you’re listening to. Hifiberry’s DAC + DSP, for example, combines DSP and analog translation capabilities into a single device, removing the need for two separate devices.
The offering, however, is noteworthy in that it also includes a blank slate. There are no pre-installed programs or applications on Hifiberry’s DAC + DSP. Due to the small size, there are limitations to how much you can accomplish. On the other hand, simple room balancing, up sampling, or down sampling should be no problem.
Conclusion
A digital signal processor is a technological advancement that can perform many alterations and modifications to a digital output fast and precisely. DSPs can improve sound quality in audio equipment without meddling with voltages the way analog gear does.
Although there are advantages to employing a DSP, others believe that it isn’t necessarily an improvement for the overall listening experience. After reading the previous explanation, what are your thoughts about DSPs? Do notify us!
You may also be interested in:
