Most speakers that are sold in the market today have a certain threshold, where they have a maximum volume that they can produce when playing audio files. When that certain threshold is met and broken, often, most speakers will produce a crackling or even a popping sound when playing an audio file.
This can be quite disturbing to many, especially for those owning expensive speakers or having an extensive speaker setup such as a home theater system in their home, for example.
But not all people know why this kind of issue persists with many speakers, whether it would be a newer model or an old, dusty one. Is there a certain reason as to why this is happening even in newer speaker units? And can the threshold of the maximum volume output be increased in some way to avoid the crackling issue?

Main Causes For Speakers To Crackle and Pop
As mentioned earlier, most speakers will have the crackling or popping issue after the maximum threshold for volume output has been breached. However, that isn’t only the main reason why that kind of phenomenon is happening, as there are also other factors to consider as well.
One known reason why speakers crackle or pop at certain volumes is due to the interruption of electric currents used as audio signals to the receiver of the speaker unit. This issue is commonly known as an “interrupted current,” wherein several factors for this happening such as faulty cables, improper connections, and issues with either the receiver (speaker) or from the audio source.
Do take note that speakers are considered to be transducers, wherein they convert electrical energy (also known as audio signals) into mechanical wave energy (which are basically sound waves). Those are the sounds that are produced by the speakers that we hear. It is notable that audio signals have alternating currents on them.
How Audio Signals are Being Disrupted or Interrupted
You may wonder how audio signals are disrupted. The simple answer to that is the linear movement of the signal is disrupted or interrupted during its travel to the sound driver of the speaker unit.
To obtain a smooth sound wave output, the said linear movement must be free of obstruction, or else it will produce the crackling or popping issue as a result.
To put it simply, the image on how an audio signal should travel from the audio source to the speaker unit should look like this, which is called sine wave:
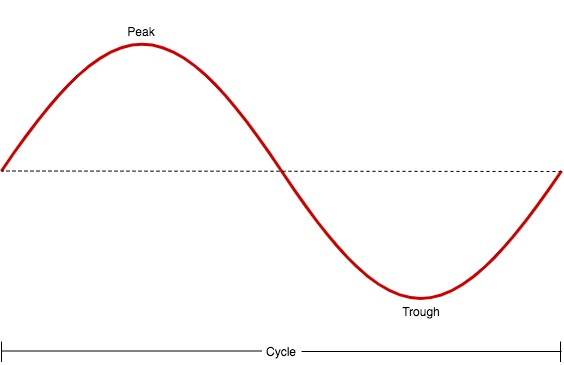
However, if there is an obstruction on the transmission of the audio signal to the speaker unit, the sine wave will look like this instead:
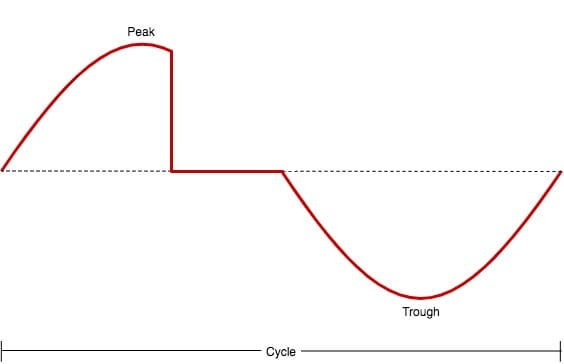
The disturbing portion (the reversed L line shape) on the sine wave image chart above represents the disruption in the transmission. That is also where the crackling or popping issue comes from.
Do take note that the dotted line on the center has no voltage on it, meaning that no signal will pass through that point (remember that audio signals are basically electric currents).
Since no audio signal passes through the center wherein there is no voltage for it to pass through, it will result in the popping sound that we hear from our end. But, take note that it isn’t the primary reason for that, but instead of the speaker unit thinking that there are no audio signals passing through its receivers.
However, the Sine Wave image chart is vastly different when it comes to the crackling issue of a speaker unit, which looks like below:
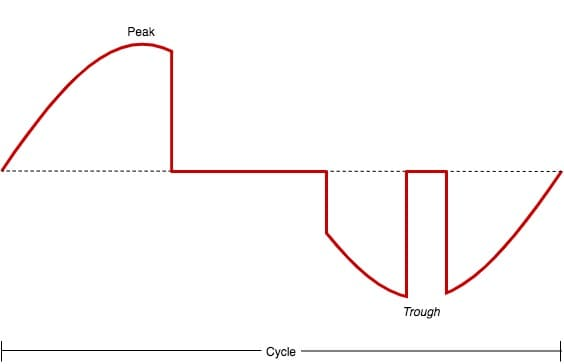
As seen from the image chart above, instead of a single interruption, there is now a second one that also lands on the centerline, wherein there is no voltage for the signal to pass through. Due to that phenomenon, the speaker will tend to pop in multiple succession. That is what we call the “speaker crackle,” or, to put it simply, the crackling issue.
Why Do Digital Crackles or Pops Still Happen?
You may only think that the crackling and popping issue only happens with analog players, but it also happens to digital players that use a digital-to-analog converter.
When a digital audio signal is suddenly cut off, it will then produce a digital crackling/popping issue as a result. To avoid this issue, many editors are using crossfading when they are editing audio files.
Why Do Vinyl Records Crackle or Pop?
It is a different case for its crackling/popping when it comes to physical audio players such as a vinyl record player. It is a different case for its crackling/popping. Instead of interrupting audio signals during playback, the reason for the said issue is simply due to the “noise” in the signal itself. The noise can come from the static electricity that the record has and the dust covering it.
Do take note that vinyl records, by default, hold a small amount of static electricity. It is then picked up by the needle that “reads” the vinyl record, which will produce a crackling/popping sound in the player’s speaker. Therefore, it is nigh impossible for a vinyl record to be crackle/pop-free once played.
However, as mentioned earlier, dust along with dirt and debris also play a major cause for vinyl records to crackle/pop during playback. Those are usually found in the groves of the record itself, which are usually microscopic in nature.
You can lessen the crackling sound by using a specialized anti-static brush to clean the record before usage. There are several brands of specialized brushes for that purpose that you can find online.
Can the Crackling and Popping of Speakers be Fixed?
To put it simply, the simple answer is yes. Previously above, it has been shown that the crackling/popping issue can be fixed on physical audio players such as a vinyl record player. And for digital audio, the preferred and best way to fix the issue was through the usage of crossfading during the editing process. But how about fixing speaker units?
For various types and kinds of speaker units, the simple fix for those is by simply fixing and properly rearranging the cables that connect from the audio source to the speaker unit itself. Having a busted or broken cable will certainly produce those crackling/popping noises.
However, cables that are not properly arranged can also cause that issue, as bends and knots to the cable itself can also be the cause of the crackling/popping issue (due to possible broken wirings inside).

You can determine if the cable connection being used is faulty by wiggling it while connected and playing an audio file. If there is suddenly a crackling/popping sound while wiggling the cable connection, that means an area of the cable is faulty, most likely damage to the wires inside.
If there is no crackling/popping sound when the cables are wiggled, the next thing to check is the connection ports, specifically the point wherein the cable’s end is soldered. If the soldering connection is poor and improperly done, it will highly cause the issue instead. Re-soldering the connection is the best solution for this.
Another thing to check out when trying to fix this issue is by checking the connection ports, such as the audio auxiliary ports (or commonly called audio jacks by others). Additionally, it is best advised to also check your amplifier by this time, as it can also be the source of crackling or popping. Basic troubleshooting can significantly help in this case.
It is best advised to purchase and install a new audio cable for connection if the issue persists even after fixing the connection and basic troubleshooting has been performed on both of your audio source and the speaker unit connected to it.
Is the Distorting of Speakers at Higher Volume Related?
As mentioned at the start of this article, the common reason why the crackling/popping issue happens with speakers is due to the threshold of the maximum volume it can produce without the issue coming out. However, many might think that the distortion of speakers is the one to blame for the crackling/popping issue of various speaker units. But is it really related to that?
The basic answer to that question is simply yes, as the distortion problem itself is similar to the problems and root causes of the crackling/popping sound issue (i.e., faulty wiring, bad connection, issues with the speaker unit, issues with the speaker unit with the audio source, etc.).
But, keep in mind, there are two commonly acknowledged reasons as to why the audio output of speakers tends to distort at higher levels, which are the following:
- The audio source itself is distorted. Most likely, the audio file being played by the audio source has distortions within it.
- The drivers of the speaker unit cannot handle the given load of the audio source, producing a distorted audio output as a result of the drivers being pushed over their maximum limit.
What is Audio Distortion?
To imagine what an audio distortion looks like, you may refer to the Sine Wave image chart previously shown above. That is basically a waveform, wherein any kind of deformation to that will cause the audio output of the speakers to distort at the end of its transmission process.
The deformation, in that case, is where the smooth travel of the S-shape line is suddenly cut and changed to a different shape and direction.
However, do not confuse the term “audio distortion” with “speaker distortion,” as the latter is a different story altogether. A speaker distortion means that there are differences in the waveform it produces that are significantly different from those produced by its driver.
This kind of distortion is also the one that many commonly hear (i.e., audible distortion) from speaker units as the sound output. But not all can hear and identify it immediately, as only trained ears can clearly tell whether distortion is happening or not on a speaker.
Other sources of possible sound distortion of a speaker unit are the following listed below:
- The original audio signal of the audio source.
- The various amplifiers that are connected between the audio source and the speaker unit, specifically faulty amplifiers.
- The present and active crossover networks that both the audio source and speaker unit are connected to, specifically faulty network connections.
- Physical damages to the speaker unit itself.
Do take note that even if one of those four mentioned above produces distortion (wherein most of the four work together as one), the speaker unit will highly produce distorted sound itself as a result.
How To Fix Speakers Crackling & Popping
To avoid having distortions on your speaker units, there are two things that you need to keep in mind when you want to use them to their full potential. Those two things are having the correct and matching amplifier for your speaker unit and disregarding the power handling that many amplifiers have in their specification sheet.
First, having a properly matched amplifier can mean a huge thing when it comes to using your speakers for audio playback. Without a proper amplifier to support your speaker unit, there is a high chance for it to have the sounds and audio being played by it to be distorted as a result.
Second, disregarding the power handling of amplifiers for your speaker unit is a must. It doesn’t matter if the amplifier’s power handling is lower or higher than your speaker unit (i.e., your amplifier has 200-watt handling, while your speaker unit only has 100-watt handling); the sound or audio will still be distorted regardless. See our article on speaker impedance for more details.

If that happens, the only logical next step is to turn the volume down significantly until the distortion is gone. It is basically the golden rule when it comes to the connection between amplifiers and speakers.
Thirdly, a fix may be as simple as replacing an auxiliary 3.5mm TRS cable and/or replacing any loose or faulty connections. To find out which wire may be at fault, it may be helpful to move each wire at lower volumes to see which one could be causing possible distortion.
Why Does Distortion Happen at High Volume Levels?
As mentioned in the cause of speakers crackling or popping, there is a specific threshold of maximum volume that a speaker can produce when playing an audio file. This is the same when it comes to distortion, wherein it has its own threshold limit.
But instead of the maximum volume it can handle and produce, it refers to the maximum output an amplifier can handle and produce, wherein it is passed to the drivers of the speaker unit.
When a certain threshold for the amplifier is reached and broken through, distortion will take place as a result of it, and it is usually called “amplifier clipping.” The image chart below shows how the distortion occurs in a waveform flow, similar to the Sine Wave flow:
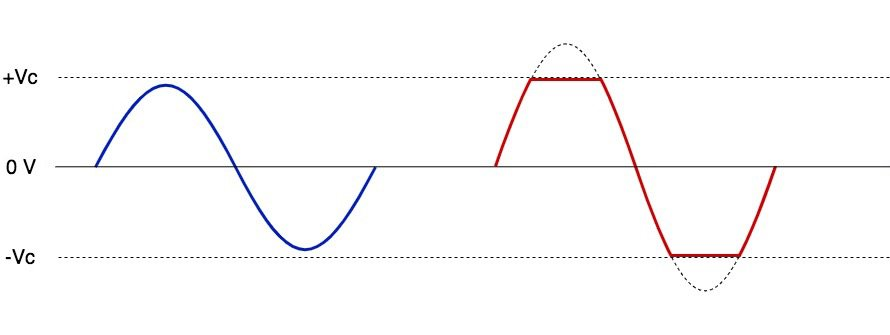
Do take note in the image chart above that both the +Vc and -Vc are limits of what an amplifier can produce as signals that will be then transferred to the speaker’s drivers.
As mentioned with the Sine Wave image chart explanation, both the upper and lower dotted lines represent no voltage in that area, meaning that no audio signals (which are electrical currents) cannot pass through. This means that the output produced by the amplifier will be lost at that part, commonly called “clipping voltage level.”
Additionally, do take note that the blue line represents an unamplified audio signal, wherein it meets the threshold limit of the amplifier. The red line, however, represents the amplified state of the audio signal, wherein the amplification level is beyond what the amplifier limit can handle.
The red line happens when the volume is greatly increased by the user, which the gain for that audio source is amplified by the amplifier unit to match the command in the increase of volume as a result. Lowering the volume will turn the line to blue eventually, wherein the amplification will be lowered to match the decreased volume level.
Speaker Distortion Is Related to Speaker Crackling and Popping
As we can see from the information above in this article, the crackling and popping issue of many speaker units in the market today are somewhat related to speaker distortion and vice-versa.
Both issues almost have the same explanation as to why they are happening, albeit having different root causes of the issue and explanations as to why the problems are happening for each issue.
Still, the ways and solutions in fixing both problems are similar in nature; most of them involve the components of the problem, such as the audio source, the connections used, and the driver speakers. The only noticeable difference when it comes to the components of the two issues is the other involves amplifiers, while the other obviously doesn’t.
The best way to avoid having either issue is to make sure that all components are working well and are in top condition while having the best and proper connection between each component. Additionally, make sure that all of those components are damage-free.
People Also Wonder:
1. Is Crackling Bad For Your Speakers?
Depending on the loudness of the crackles and pops, there is some potential of it damaging your speakers. Though a majority of speakers have inherent protection circuitry, it is advisable to fix the issue as soon as possible to limit any unnecessary damage through extended use.
2. Why Does My Speakers Sound Static?
One of the most frequent causes of static sound in speakers is a loose connection. Hence it is important to make sure that the cables with connectors are secured appropriately to the speaker ports. It is also important to remove any speakers from any electrical interference which may also contribute to this static sound.
Conclusion
Speakers crackling or popping can be a frustrating experience that detracts from the overall listening experience. Having properly matched amplifiers, a secure cable connection, removal of electrical interference are just some examples to troubleshoot the ongoing crackling. The several fixes mentioned in the article can help eradicate this issue once and for all to ultimately deliver the best sound from your equipment.
You may also be interested in:
- 5 Different Types of Headphone Drivers
- How To Increase Bass on Windows 10
- Speaker Impedance Explained
