As an audiophile, having the perfect audio experience is a must when it comes to picking out headphones and speakers. Many do not realise that having a good amplifier for headphones will not only drive them to sufficient levels but make them sound better. In the same way, amplifiers are a crucial component to drive loudspeakers to appropriate levels.
There are two types of amplifiers for discussion within this article – tube amps and solid-state amps. What exactly are these type of amplifiers – and which should you choose in your quest for the perfect sound?

Headphone Amplifiers: What Are They For?
Before we head deeper into the differences and purpose of both tube amplifiers and solid-state amplifiers respectively, we must tackle first what are headphone amplifiers (amps for short) and what it does specifically for your headphones.
Headphone amps are basically low-powered amplifiers designed for headphones instead of speaker units such as your home theater system and other similar plugged-in-based audio peripherals. The general purpose of headphone amps is to increase the low-voltage audio signals that can be easily converted by the main speaker drivers of your headphones.
Most headphone amps are smaller and portable in nature, unlike regular amplifiers which are usually dependent on being plugged all the time to a power source (i.e. wall socket).
For headphone amps, they are usually powered by their own internal battery which is usually lithium-ion batteries (i.e. the battery of your smartphone). However, there are some older designs that rely on traditional cell batteries such as AA or AAA batteries.
But the mentioned details of amplifiers above are for newer, modern headphone amps. There are still some older designs that have their own structure layout than their modern counterparts. We will look into those, but first, we need to look into another important topic in understanding how amps work.

What Do Headphone Amplifiers Do?
The basic answer to that question is that it makes your headphones work and sound better by improving the overall sound quality that your headphones produce. However, as for the technical answer to that question, be ready to take down some notes if you want to be a true audiophile.
What a headphone amp does in technical terms can be explained by the following: the amplification level and performance that it can provide to a headphone is heavily reliant on the quality and specifications of the headphone that it is paired with. It goes without saying that the output of the amp will suffer greatly when paired with faulty and/or low-quality headphones.
Headphone Impedance
Furthermore, many audio peripherals such as headphones rely on impedance that is often built inside them. The term ‘impedance’ means the resistance to the current an audio peripheral has. The average headphone impedance is 32 Ohms with the average consumer-orientated tending to have lower impedance levels.
Audiophile headphones tender to have higher impedance levels requiring more amplification to drive them. However, there has been a trend for more efficient headphones with a strive for lower impedance levels.
Speaker Amplifiers: What Are They For?
Speaker amplifiers are also known as power amplifiers and are used to enlarge or amplify small electrical signals sufficient enough to power a loudspeaker. This may also involve pre-amplifiers enlarging signals to line level enough to be accepted by a power amplifier.
The reason why speakers need amplifiers is so that the input signals are appropriately converted to stronger output signals to sufficiently drive loudspeakers to make them sound proper. The ratio of input signal to output signal is known as gain and it is up to the amplifier to provide the right level of gain to amplify the input signal.
There are different terminologies in the audiophile world and hence it is important to get them correct when setting up your home theater system. For example, power amplifiers are not the same as integrated amplifiers. Integrated amplifiers often marry pre-amplifiers with power amplifiers and contain built-in digital-to-analogue converters (DACs) as well as phono stages for turntables.
Modern ones also have integrate USB function as well as Bluetooth & networking streaming.
An A/V Receiver on the other hand is a device that is able to receive an audio signal, process it and amplify it to the loudspeaker. It is also able to allow video to pass-through to a TV or projector which separates it from a power amplifier.

Speaker Impedance
It is important to properly bridge impedance between a power amplifier and a loudspeaker. Manufacturers make this process easy by listing impedance on their amplifiers. Doing so prevents any damage to the driver components of a speaker and limits clipping at higher volumes. See our article on speaker impedance for more details on how to do this.
How Amps Process Currents
The whole process works by transferring the audio output from a connected source to the amplifier. During the transfer process, the voltage levels are increased enough to power up the transducer (headphone or speaker) to produce the audio output on its end.
We are now going to look into two types of amplifier: the tube amplifier and the solid-state amplifier respectively.
Solid-State Amplifiers
The first type of amplifier that we are going to talk about in this article is the solid-state amplifier. Even though it might not be noticeable at first with its name, this kind of amp uses a transistor circuit as a power source for altering electrical signals to audio signals.
How Does a Solid-State Headphone Amp Work?
The internal structure and layout of a solid-state headphone amp are akin to a sandwich, wherein there are three layers of silicon inside that “sandwich” structure. Two of those layers are negatively charged (the outer layers in most cases), while the remaining layer is left as it is.
However, due to it being sandwiched by two negatively-charged layers, the silicon layer in the middle is positively-charged that acts as a barrier between the two as a result.
Do take note that the negatively-charged layers produce electrons that conduct electricity and those pass through the middle layer through holes in its design. That lets the electrons pass through, allowing the processing and transfer of electrical signals that are altered to become audio signals.
The first silicon layer that is negatively charged is called the emitter, the middle positively-charged layer is considered as the base and the last outer negatively-charged layer is called the collector.
Powering up the whole solid-state amplifier is the previously mentioned transistor units inside it. The units themselves have a base electrode in them as part of the power source.
Desktop and Portable Versions
A solid-state amp comes in two versions: a desktop version, which is much more powerful and has more features but is much bigger and lacks portability. The second version is a portable one has the basic features similar to the desktop version but is much smaller, powered by its own batteries, and is portable. Additionally, portables are way cheaper than desktops.
Speaker amplifiers tend to be larger than headphone amplifiers and most adopt desktop real-estate.

What Are the Pros and Cons of a Solid-State Amplifier?
When it comes to the pros of this kind of amp for your headphones and speakers and your listening experience, you will surely be happy to hear accurate sound from every playback. Second, it has a cleaner audio output and transparency when it comes to its performance. Lastly, most headphone amps of this design are lightweight and are compact in nature. Additionally, most amps of this kind are way more affordable than the competition in the market nowadays.
The only known cons of using this kind of amp for your headphones is that the parts for replacement/repair for this type of amp are harder to find than the others. It also has issues with higher volume levels, as it tends to crack up and dip in quality at near max levels.
Tube Amplifiers
As mentioned earlier, there are various types of amps that a consumer can purchase on their end. Although, there are two distinct types of amps one should be aware of, as either one provides a different kind of setup and performance against each other. The first one that we will be discussing is the tube amplifier.

The picture above shows a sample of a “traditional” tube amplifier for headphones. Also known as vacuum amps / vacuum tubes due to its design, this kind of headphone amp doesn’t look portable at first, however, recent models of this kind of amp have been given the portable treatment as seen on the image below. The image below is a newer and modern design take on the tube headphone amp, making it small enough to be portable for everyday use and travel.
Portable or not, there is one aspect that they keep and that is the noticeable and eye-catching tubes shaped like an elongated light bulb that is part of the amp itself. The purpose of those vacuum tubes is to amplify the audio output from the source by controlling the electrical current. During usage, those vacuum tubes light up with a particular glowing color implemented by its manufacturer.
Tube Amplifier: Design
The insides of a vacuum tube of a tube headphone amp have a cathode, anode, grid, and some components for audio processing and transfer. It also contains rarefied gases used for the entire process. Thanks to the nature of the vacuum tube, its environment inside allows the flow of electric currents for audio.
The Influence of Tube Amplifier on Audiophiles
Tube headphone amps have been a popular choice amongst audiophiles all around the globe, as their audio output and performance are one of the best when it comes to amps for use in headphones and speakers. The smooth and responsive sound that it delivers makes sure that the sound and music coming out from the connected headphones and speakers is euphonic with a great tonal quality.
What Are the Uses of Tube Amplifiers?
Just like any form of device, there are several uses for a tube headphone amp (mostly of those are audio-related though). However, for those who are into music such as audio engineers and audiophiles, the various uses of this amp will be greatly beneficial for them in the long run.
- For mixing and critical listening. This is perfect for audio engineers or for those who have a sound-related profession, this usage can help check the balancing of audio, regardless of how many elements are used in it during pre-production.
- For studio recording and tracking. For those in the music industry and running a studio recording business, having this type of amp is a must as it allows numerous simultaneous usage in a single tube amp during recording sessions.
- For musical performances. When it comes to communities and circles using high-end and premium hi-fi headphone units, having a tube headphone amp is akin to a requirement to get inside their group as many music performers and professionals use this kind of equipment throughout their whole career, especially with some of their performances.
What Are the Internal Components of a Tube Amplifier?
If you are curious about the inside of a tube amplifier, no need to look further as we are going to explain the commonly found parts inside of it and their purpose.
- Cathode. An internal pole that is positively charged. It is the heart of any vacuum tube.
- Heating Filament. Being placed right next to the cathode, its function is to increase the heat levels of a cathode for electrons to flow through it freely.
- Plate. A component that surrounds the whole inside of the vacuum tube, it contains a high positive charge for the overall process.
- Grid. A component that is placed between the plate and the cathode, it is usually made from a piece of metal that is connected to the input of an audio source and is usually negative in nature until used during the process to keep electrons.
- Capacitors. A component that stores electrical charge is responsible for the steady release of those into the vacuum tube. This is one part that has a high voltage stored even after the device is turned off, so touching this without proper training is ill-advised.
- Resistors. A component designed for voltage and current regulation inside the vacuum tube amplifier with their resistive value (that is also meant for dispersing electrical energy).
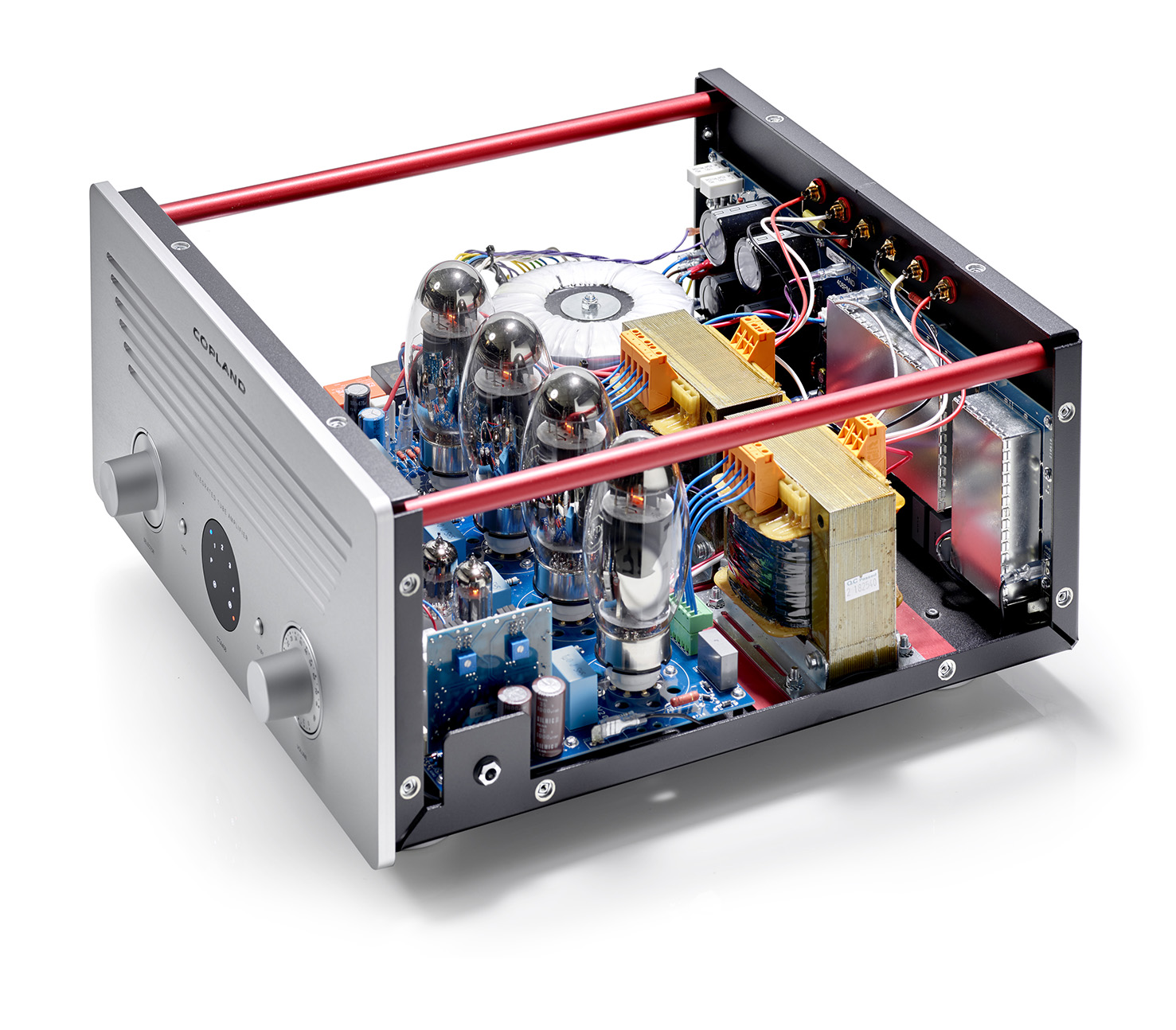
What Are the Pros and Cons of a Tube Amplifier?
Just like any gadget or device, a tube amp is liable to pros and cons respectively. To start with the pros, this type of amp can provide additional warmth to tame headphones and speakers with bright sounds as its output. The sound produced by this amp is inherently much stronger than other amps, particularly from a solid-state headphone amp. Lastly, the aesthetics and design of a tube headphone amp (especially with colored vacuum tubes) can be a sight to behold.
When it comes to cons, due to the design nature of this amp, it tends to have heating-related issues/problems (i.e. overheating, etc.). There is also a prevalent distortion issue and can be only fixed by using a transformer with it. Lastly, most tube headphone amps are bulky and heavy in design by default (even with the portable versions).
Tube Amplifiers: What’s The Point of Them?
To be clear, most new and modern devices such as phones and laptops that you can purchase from the market today have their own built-in amplifiers. Although not as powerful or crisp as a dedicated amp unit, those can still pack a punch when it comes to standalone audio output and performance. So why purchase an amp in the first place, particularly why a tube amplifier?
The answer to that is simply that headphones, especially high-quality and premium hi-fi models, need a proper amplifier to draw out their full audio output and performance. Remember that some headphones are built to have high impedance levels, meaning that it needs a large amount of amplification power for the best audio output.
The drawback to that is the headphone itself is a device that drains a lot of power in order to bring out its full potential as previously mentioned.
Although having that kind of drawback, hi-fi headphones are still used majorly in the music industry and in sound-related jobs/professions. Many music artists, professionals, music studios, and studio productions heavily rely on those kinds of headphones.
If you want to experience the full audio output and performance potential of your headphones, it is highly advised to use this kind of amp. You won’t regret getting this kind of amp even though it is expensive as the experience that you will get will surely outweigh that.

In the same way, speakers may also pair well with tube amplifiers given the unique euphonic timbre that they can produce. Many audiophile enthusiasts use tube or valve amplifiers owing to their ability to produce this rich and engaging sound.
However caution should be advised as a tube amplifier can cause damage to speakers if there is impedance mismatching and the minimum impedance of the loudspeaker is too low. Best sound results are also obtained with the impedance being as flat as possible – without large fluctuations. See our article on speaker impedance for more details.
Tube power amplifiers tend to have higher output source impedances or lower damping factors owing to their lower negative feedback and output transformers. This is contrast to solid state amplifiers which tend to have near-zero output impedances. The effect is that tube amplifiers have lower frequency damping which can have add some bloom to bass – a quality which some may prefer.
Even-Order Harmonic Distortion
The reason why tube amplifiers sound different to solid-state amplifiers is that they produce a certain type of second-order distortion. While on paper, audio purists may be offput by the lab measurements of tube amplifiers, this type of distortion is often referred to as ‘harmonic distortion’ for its pleasing and musical timbre.
This type of distortion increases as volume levels increase in much the way as an instrument during a musical performance. This gives the characteristics of longer sustains of notes whereas solid-state amplifiers have sharper and more refined transients.

Tube or Solid-State Amps: Which Should You Choose?
When it comes down to choosing either a tube or solid-state amp, your preferences in audio output and performance will be the ultimate deciding factors. Another thing that will help you decide when choosing between the two is the pricing; although neither both are economically cheap, one is basically cheaper than the other overall.
To simplify things on your end, just remember the following when it comes to choosing either one of them for your headphones and your audio listening experience:
Choose Tube Amplifier if:
- You prefer the warmer, vintage-sounding performance and looks.
- You are okay with properly maintaining the device with occasional tube changing.
- You can afford their relatively higher expense.
Choose Solid-State Amp if:
- You prefer more accurate audio output from your headphones/speakers without coloration.
- Portability is an important consideration (especially with headphones)
- You prefer having a newer, modern device and hate device maintenance.
Hybrid Amplifiers
A third type of amplifier that has cropped up is the hybrid amplifier which makes use of both tube and solid-state functionalities to create its overall sound. One example of this is the iFi Pro iCAN amplifier which combines a purely solid-state J-FET based circuit of fully-discrete Class-A topology and a J-FET switchable to valve Class A based dual GE5670 tube input.
The obvious advantage is that users are able to tweak the sound output to their preference at the flick of a switch. However, hybrid amplifiers tend to be more expensive than their solid-state or tube amplifier counterparts owing to their difficult engineering processes.

Conclusion
Deciding between tube amplifiers and solid-state amplifiers is an important consideration when driving your headphones or speakers to sufficient levels. While neither is inherently better than the other, both offer their unique advantages which some will no doubt prefer over the other. Tube amplifiers for their vintage look and musical sound whereas solid-state amplifiers for their clean and precise audio output. Hybrid amplifiers are few and far between but combine the best of both world worlds with their added convenience and functionality.
Nowadays, it’s better to have proper knowledge about setting up your home theater which will serve you for many years to come.
You may also be interested in:
- Best Integrated Amplifiers Under $1000
- Amplifiers vs Pre-Amplifiers
- Speaker Impedance Explained
- Headphone Impedance Explained

Tube amps uses high voltage, it had very wide linear zone, 400-600V vs solid state 12-40V that significantly different sound hearing. Other technical design also important, most tube amps are non NFB (negative feedback), class A design vs solid state class AB, & screaming with
bulky output transformer vs final transistor. Tube amps doesnt match with any digital music with so much subwoofer boom within
Thank you Basuki, all very valid points – particular about the technicality of non NFB and Class A/AB designs